Cell organelles
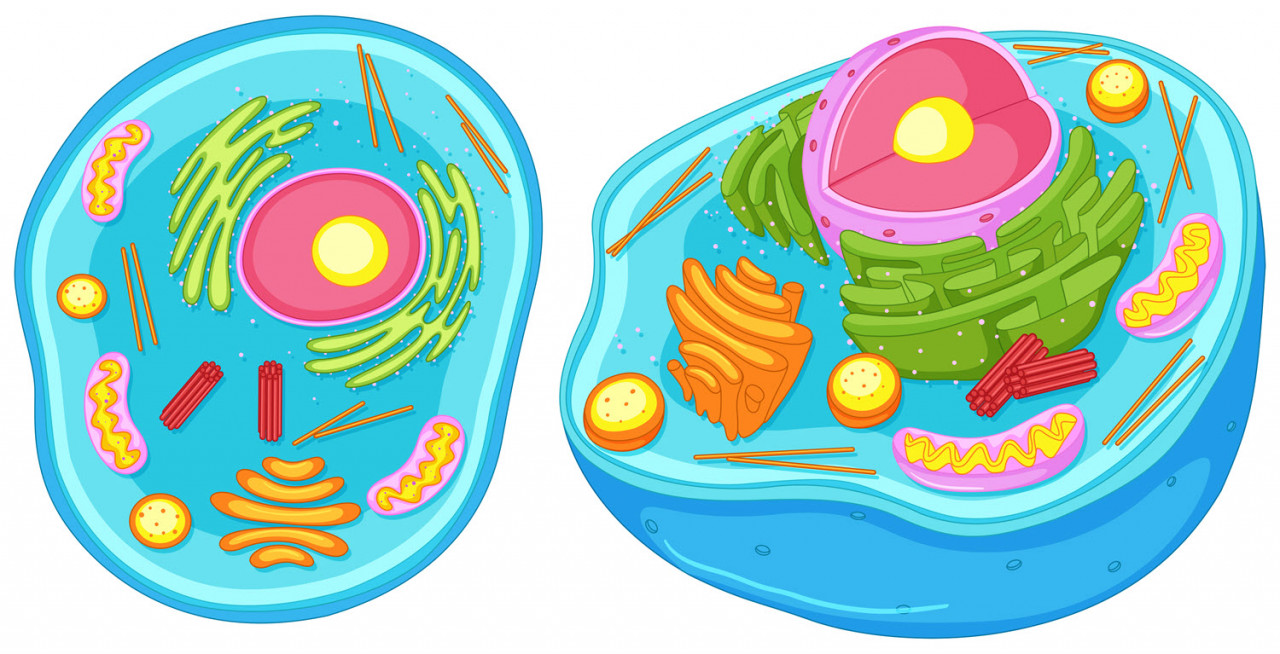
Eukaryotic cells
In this post Jayne explains the names and functions of the organelles in a eukaryotic cell.
As an A level Biology student, you may be asked to explain the relationship between the functions of different organelles in a eukaryotic cell. As long as you know the functions of individual organelles, you can soon see how they interact to make a product or carry out a function.
A typical question about eukaryotic cells could go something like this:
"Explain the function of each of the following organelles and how their roles are interrelated; The nucleolus, ribosomes, nucleus, rough endoplasmic reticulum, golgi body, vesicle, lysosome and cell membrane."
Try the following..
- Each of the boxes below contains the name of one of the organelles which can be found in a eukaryotic cell.
- Clicking on the box will reveal or hide an explanation of the organelle and its function.
- Hide the content in all the boxes
- See how many of these organelles you can define BEFORE you click for the answer
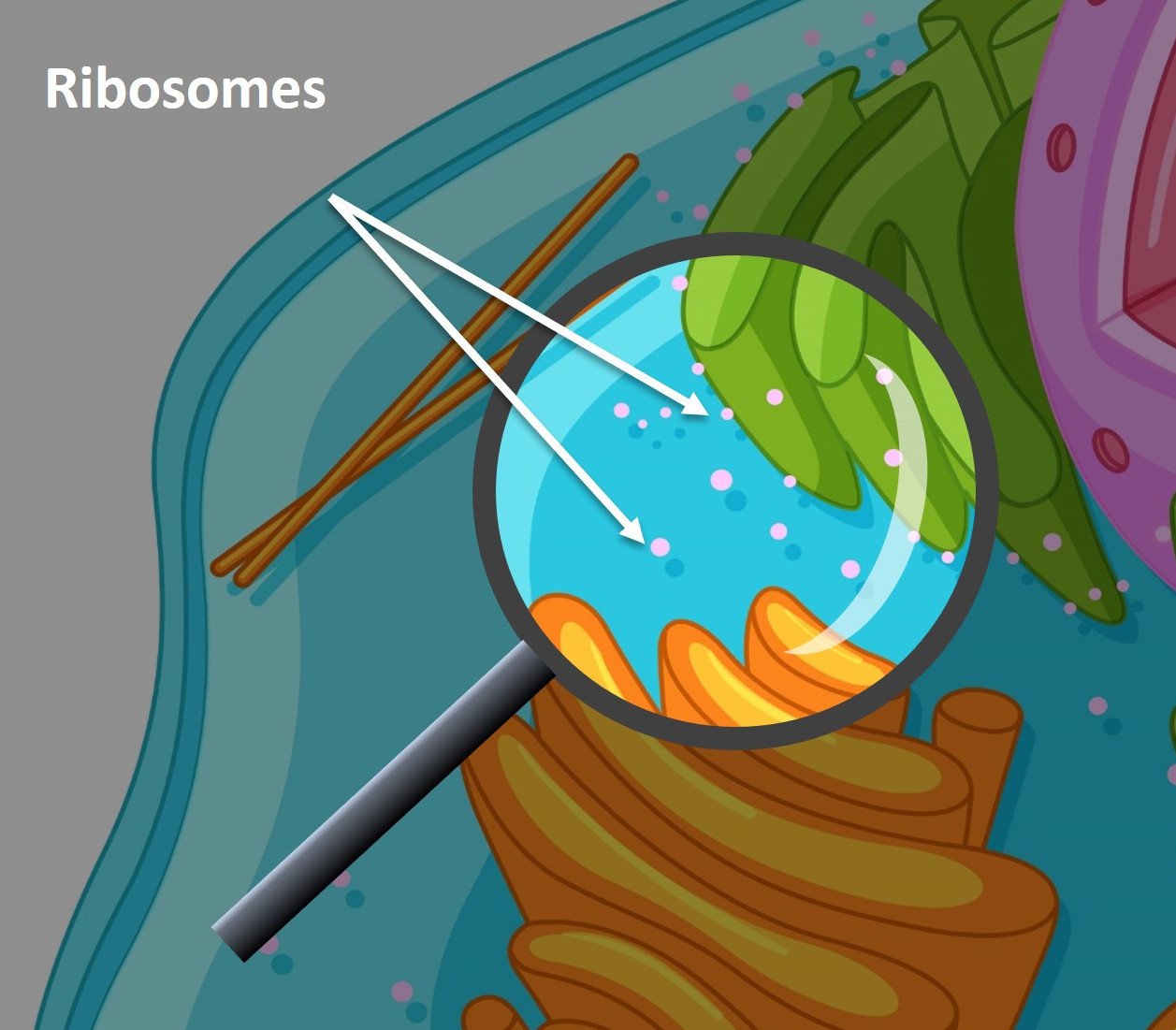
Ribosomes
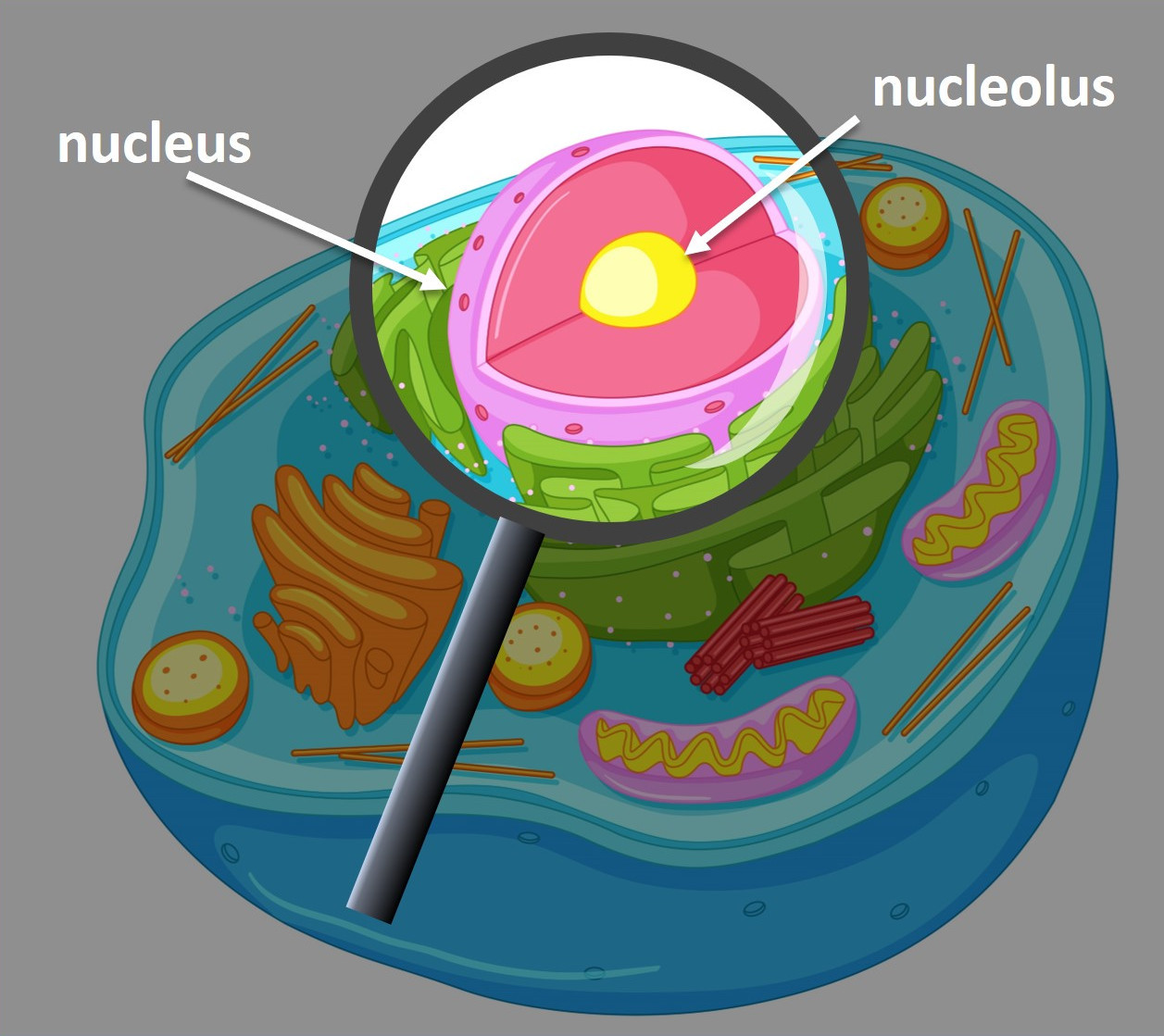
Nucleus
The nucleus contains DNA. DNA contains the codes for polypeptides. The DNA code for an individual polypeptide is copied into a smaller molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA). The mRNA code leaves the nucleus and attaches to a ribosome. A polypeptide is assembled on the ribosome using the code on the mRNA
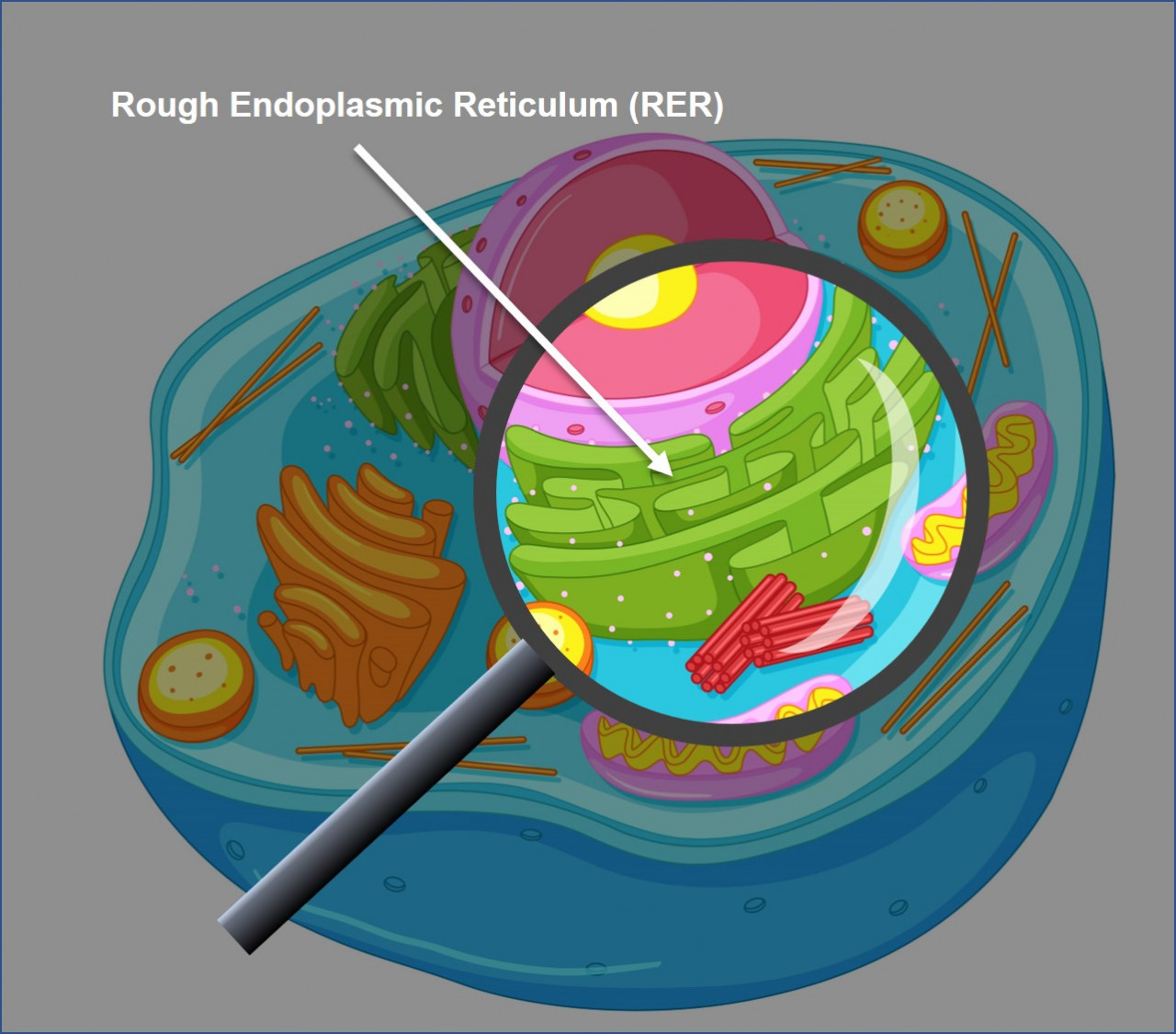
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
RER is like a big maze of interconnected tunnels made of membrane with ribosomes on its surface. Once polypeptides are made by the ribosomes, they get surrounded by RER membrane, forming a membrane sac. This sac, containing the polypeptide, is called a vesicle. The job of a vesicle is to move substances around the cell from one organelle to another.
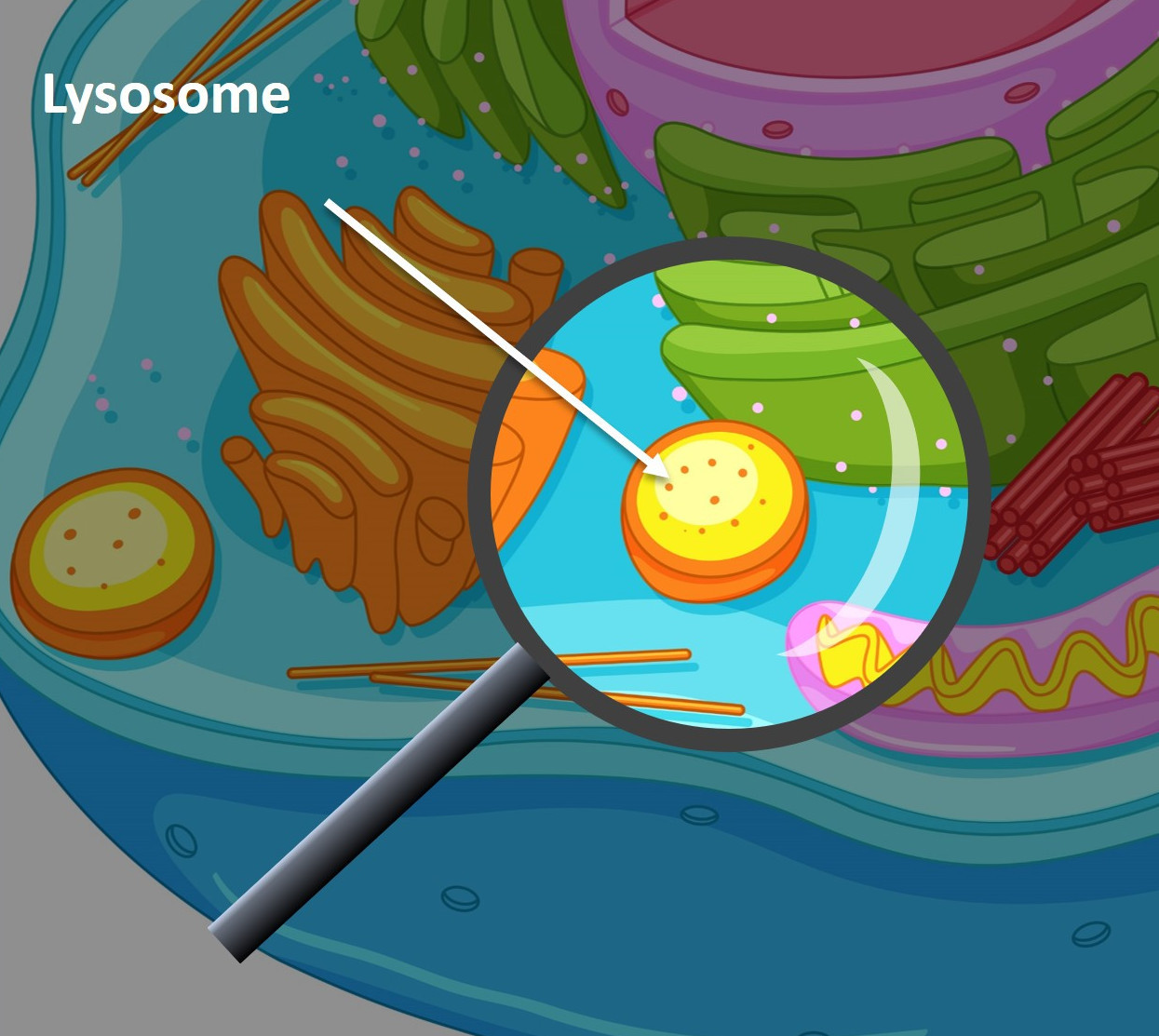
Lysosome
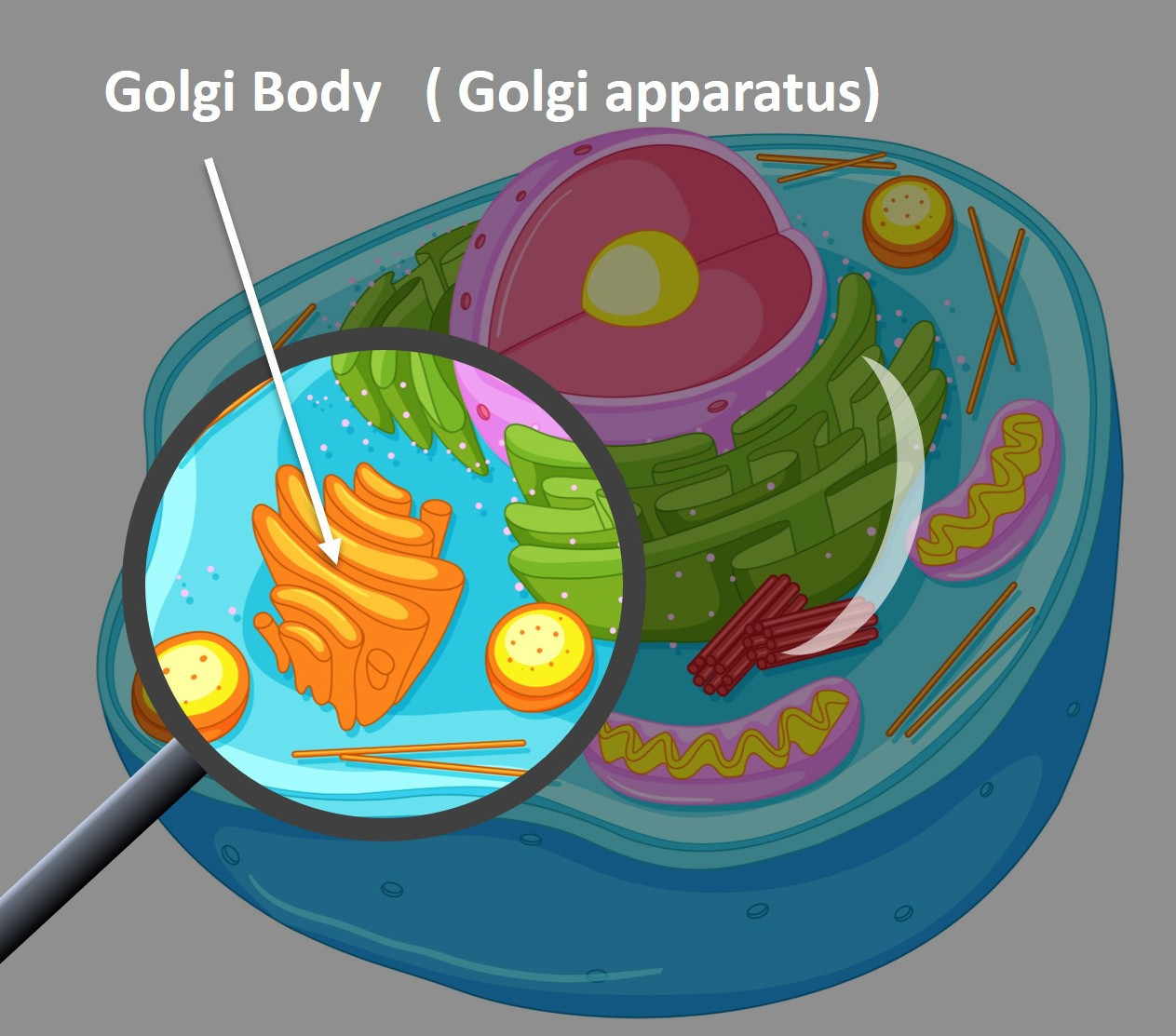
Golgi Body
Once the vesicle (containing the polypeptide) is made, it moves to the Golgi Body. The Golgi Body is a stack of membrane sacs (often said to look like a stack of pancakes). The vesicle fuses with the Golgi Body becoming part of it. Inside the Golgi Body, the polypeptide is modified. It may have polysaccharides attached to it to form a glycoprotein or it may be further folded. After it has been modified and is ready to function, the polypeptide is called a protein. The protein is surrounded by Golgi Body membrane and pinched off into another vesicle.
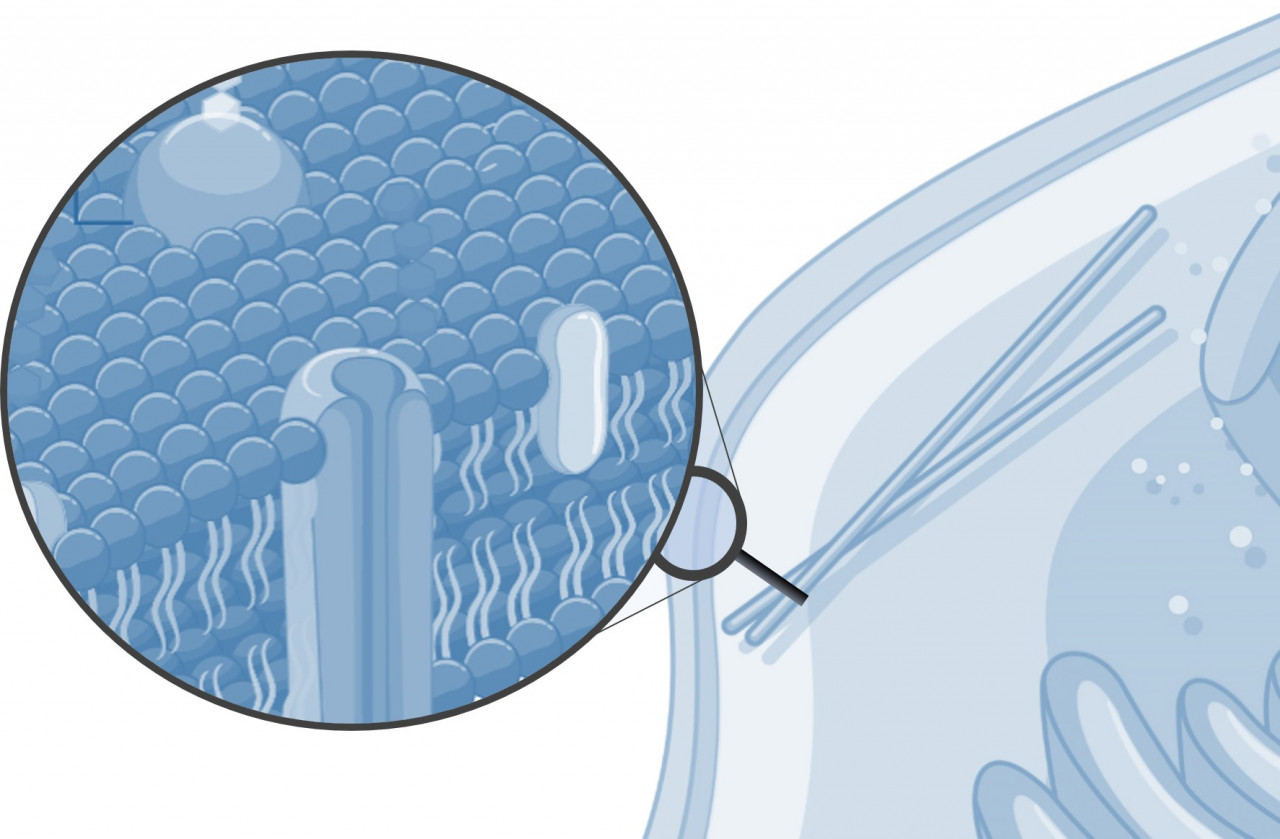
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane is the barrier between the cell and its surroundings. It has proteins embedded in two layers of phospholipid. Some small, lipid soluble and uncharged molecules can move straight through between the phospholipids. Larger, water soluble or charged ones move via various different proteins. In this way, the cell membrane is able to control what enters and exits the cell. Large substances, like proteins, that cannot move through the membrane in either of the ways listed above, move via a process called 'endo' or 'exocytosis'. This is where the vesicle fuses with the cell membrane and releases its contents into (endocytosis) or out of (exocytosis) the cell.
We will deal with the details of the cell membrane in our next post!!
To summarise, a polypeptide is coded for by the DNA in the nucleus, made on the ribosome (which was made by the nucleolus), packaged into a vesicle and taken to the golgi body where it is changed into its final form called a protein. The protein is once again packaged into a vesicle and taken to the cell membrane where it leaves the cell via exocytosis.