Carbonyl compounds
Carbonyl compounds all contain a C=O double bond. This is usually formed when an alcohol is oxidised using an oxidizing agent such as acidified sodium dichromate. The position of the C=O bond determines whether the compound is an aldehyde or ketone
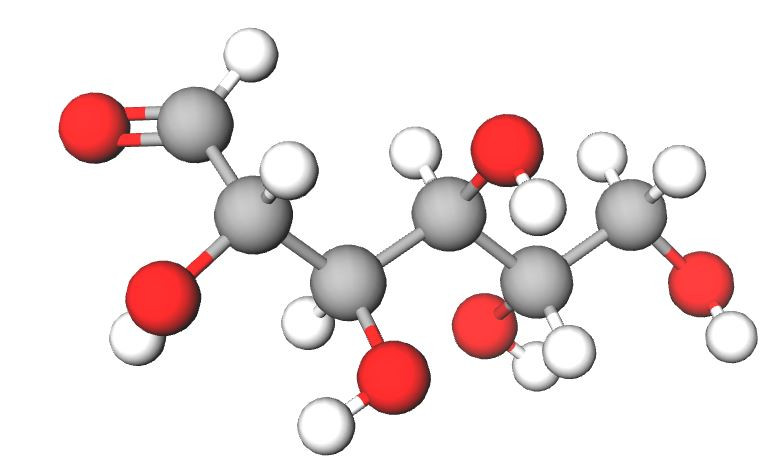
In its straight chain form Glucose is an aldose sugar which means that it has an aldehyde group which can be oxidised.
This means it has the ability to reduce other substances and glucose it therefore sometimes referred to as a reducing sugar
Making carbonyls
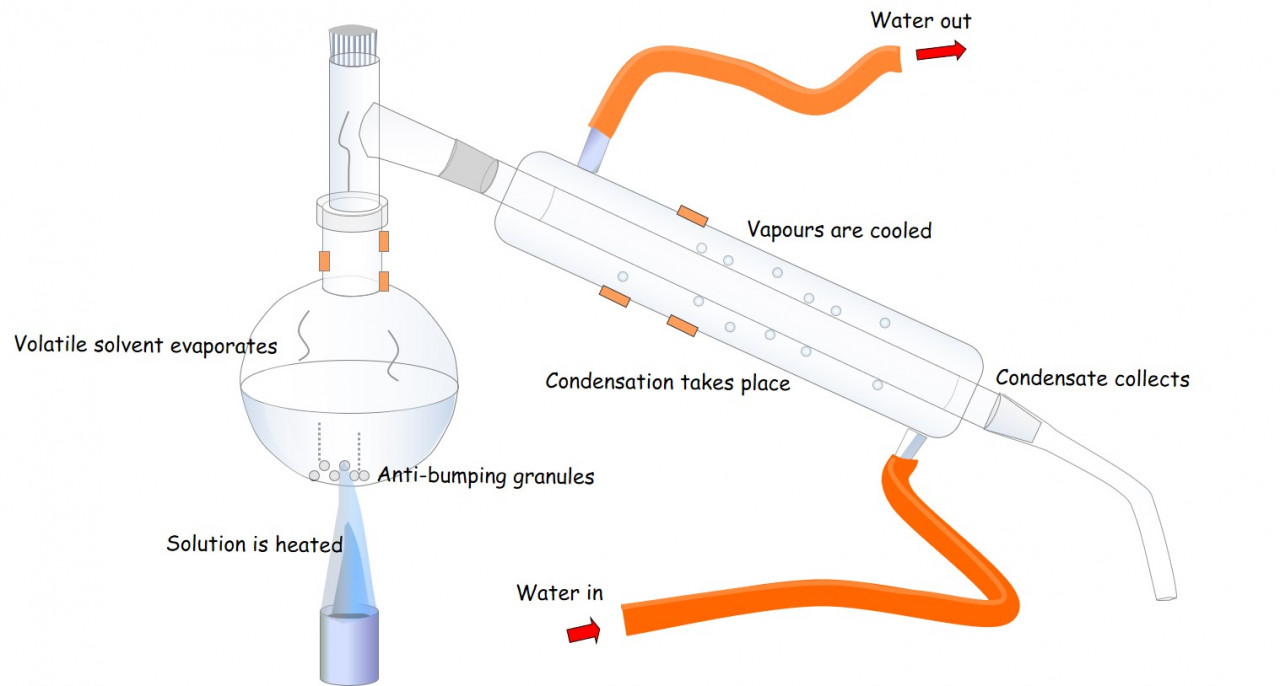
Oxidation of a primary alcohol using acidified dichromate and distillation apparatus produces a sample aldehyde.
- Ethanol will produce ethanal
- Further oxidation using reflux apparatus leads to the production of the carboxylic acid ( ethanol -> ethanal -> ethanoic acid)
- Oxidation of a secondary alcohol produces a ketone.
- Ketones cannot be easily oxidised any further.
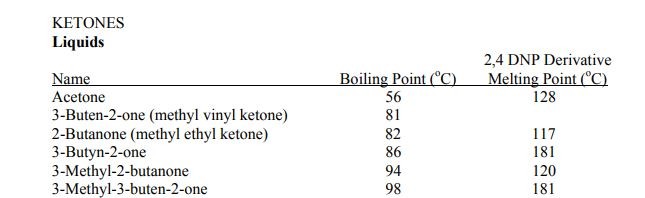
Distinguishing carbonyls
Enter your text here ...
learn these tests..
The reducing property of aldehydes compared with ketones allows them to be distinguished from each other. Both tests shown here involve reduction of the reagent by the aldehyde.
Or to put it another way - the oxidation of the aldehyde by the reagent.
- In Tollens ( ammoniacal silver nitrate solution) the silver IONS (Ag+) are reduced to silver ATOMS (Ag) which form a silver mirror.
- In Fehlings solution copper(II) ions ( Cu2+) are reduced to Copper (I) ions ( Cu+) which form a red precipitate of Copper ( I ) Oxide.
NOTE FOR BIOLOGY STUDENTS
You will have probably have heard of Benedicts solution as a test for reducing sugars. This test is very similar to Fehlings solution and gives the same results with sugars that contain and aldehyde group and are therefore "reducing" (i.e. can be oxidised).
Identifying carbonyls
Enter your text here ...
Test for further oxidation
Test for aldehyde