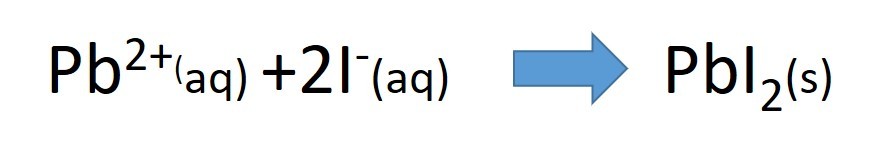salt preparation
Defining salts
Common "table" salt ( sodium chloride) is found dissolved in large quantities in seawater. Sodium Chloride is just one example of the many compounds which can be called salts. Most salts are crystalline ionic compounds
A salt is defined as :
A compound resulting from a chemical reaction of an acid, in which the acid's hydrogen ions are replaced by other (positive) ions .
Assumed background knowledge

Ionic Bonding - transferring charge
Activity The best solution?
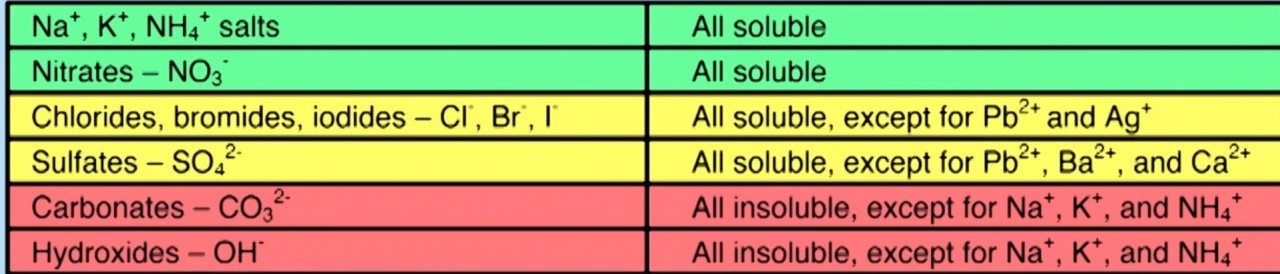
Different Ions have different solubilities . When two soluble ions are combined to form a salt the salt will remain in solution. Thus a soluble salt is formed
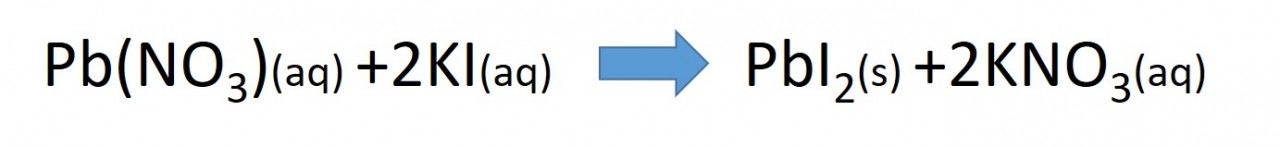
When two insoluble ions mix to form a salt, the salt forms as a precipitate.
- What can you say about the solubility of barium sulfate?
- Why is this useful?
- How would you describe the solubility of calcium hydroxide solution?
- Barium sulfate is completely insoluble.
- This means it can be ingested without being absorbed by the body. Barium sulfate is not penetrable by X-Rays. This means it can be used to find the intestinal tract in the body.
- Calcium hydroxide solution is mildly soluble.
Activity. Pretty precipitation
Activity. Predicting precipitates
Use the solubility table to predict what you would observe when you mix the following pairs of solutions:
- sodium sulfate solution + potassium chloride solution
- barium chloride solution + ammonium nitrate solution
- silver nitrate solution + copper chloride solution
- lead nitrate solution + potassium Iodide solution
- barium chloride solution + magnesium sulfate solution
Please login to obtain answers
Activity. Neutralisation
- Bases and alkalis are both capable of neutralising acids. However they are not exactly the same thing. Explain.
- What is the name and formula of the anion ( negative ion) present in all the alkali In the examples considered in the video?
- How does the concentration of the anion mentioned in 2 affect the pH of the solution?
- When acid is added to alkali, which ions combine to make water?
- Why are neutralisation reactions useful?
Acids can be defined as substances which will donate protons ( hydrogen ions H+ )
Bases are defined as substances which will accept protons.
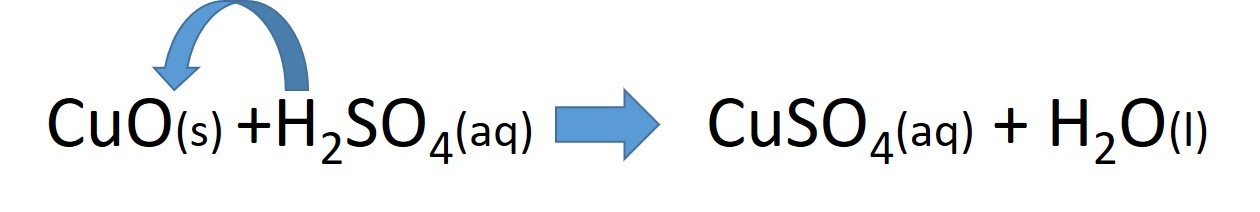
When an acid neutralizes a base, protons (H+ ions) are transferred from the acid to the base. This produces water and a salt.
Please login to obtain answers
2.37 - 2.39 Activity 5. Reacting Acids
Watch the animation carefully and write word equations giving the names the reactants and products for the four reaction types shown:
2.39, 2.40, 2.42 Activity 6. Making Soluble Salts
Study the video and use it to construct a sequence of instructions to describe how to make a soluble salt :
- Add insoluble base to a volume of the acid (50cm3) in a beaker
- Titrate the solution with an indicator in to find the volume required for neutralisation
Activity. Making Insoluble Salts
Watch the video then complete the missing word exercise below.
When an insoluble salt forms from two solutions by a ********** reaction the salt can be separated from the liquid by **********. This type of reaction is also known as a ********** reaction.
The solid salt remains as a ********** in the filter paper.
The residue should be cleaned by washing it with ********** water
It can then be dried by "patting" with dry filter paper or left out in the air to dry.
Missing words: distilled, filtration, precipitation, residue, double displacement
When an insoluble salt forms from two solutions by a precipitation reaction the salt can be separated from the liquid by filtration. This type of reaction is also known as a double displacement reaction.
The solid salt remains as a residue in the filter paper.
The residue should be cleaned by washing it with distilled water
It can then be dried by "patting" with dry filter paper or left out in the air to dry..
When you subscribe to the blog, we will send you an e-mail when there are new updates on the site so you wouldn't miss them.